What is Pepsin?
In Your Body...
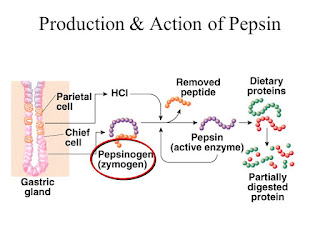
Pepsin is a digestive enzyme that performed the best in the acidic condition (pH 2) produced by the gastric juice. It digests and breaks down protein (e.g. meat, seeds, eggs, dairy products, etc.).
Keep in mind that pepsin digests proteins (not carbohydrates, not fat) into peptides. These peptides are then either absorbed in the intestine or further break down by enzymes from pancreas.
In small intestine (pH around 7), pepsin is no longer effective and no longer digests proteins.
Hormones
Hormones that regulate digestion and hunger such as gastrin and secretin stimulates the production of pepsinogen, the proenzyme of pepsin. In other words, when pepsinogen is activated, it becomes pepsin.



Comments
Post a Comment