Alkene Synthesis (Part 1)
Alkene can be synthesized by a various ways. Alkene can be made from a carbonyl, alkyne, alkane, alchols, alkyl halide and vicinal dibromides and other elimination reactions. We will split the 7 methods of alkene synthesis into 4 parts.
Part 1: Alkyl halide and vicinal dibromide
Part 2: Alcohol, alkyne and alkane
Part 3: Hofmann & Cope Elimination
Part 4: Wittig
Debromination of Vicinal Dibromides
A vicinal dibromide has two bromines connected on two adjacent carbon atoms. This reaction has a similar mechanism as the E2. The two bromines have to be anti-coplanar. A bromine atom is removed by an iodide ion (instead of a base in E2), then the other bromine leaves, a pi bond is formed between the two carbon atoms. In the example shown, note that the alkene product is stereospecific.
Part 1: Alkyl halide and vicinal dibromide
Part 2: Alcohol, alkyne and alkane
Part 3: Hofmann & Cope Elimination
Part 4: Wittig
Dehydrohalogenation of Alkyl halide
We already talk about how to synthesize alkene from a E2 (E1 is not considered because it often produces a mixture of SN1 and E1 products) reaction. Dehydrohalogenation of a alkyl halide is actually another name describing the same reaction we previously discussed in the E2 section. The alkyl halide loses a proton and a leaving group with a formation of an alkene. Remember that it is a stereospecific reaction (anti-coplanar) and the Zaitsev product is the major product (the opposite of a Zaitsev product is a Hofmann product, which is a less substituted alkene).
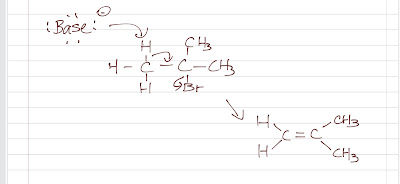 |
| E2 of a alkyl halide |
Debromination of Vicinal Dibromides
A vicinal dibromide has two bromines connected on two adjacent carbon atoms. This reaction has a similar mechanism as the E2. The two bromines have to be anti-coplanar. A bromine atom is removed by an iodide ion (instead of a base in E2), then the other bromine leaves, a pi bond is formed between the two carbon atoms. In the example shown, note that the alkene product is stereospecific.
 |
| Debromination of vicinal dibromide |


Comments
Post a Comment