Orbitals of Alkene
Alkene is a hydrocarbon with a double bond two carbon atoms. Before we can go further on the reactions of alkene. Let's briefly talk about the orbitals of a alkene.
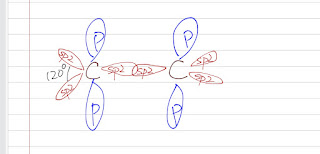 Sigma Bond: There are 6 electrons in a carbon atom: 2 in the s orbitals and 4 in the p orbitals. Take a look of ethene, one carbon is bonded to a carbon and to two hydrogen atoms and there is no lone pair of electrons at the carbon. This implies a sp2 hybridization (120º bond angle). Each C-H sigma bond is the overlap of a sp2 hybridized orbital on carbon with the 1s orbital on hydrogen.
Sigma Bond: There are 6 electrons in a carbon atom: 2 in the s orbitals and 4 in the p orbitals. Take a look of ethene, one carbon is bonded to a carbon and to two hydrogen atoms and there is no lone pair of electrons at the carbon. This implies a sp2 hybridization (120º bond angle). Each C-H sigma bond is the overlap of a sp2 hybridized orbital on carbon with the 1s orbital on hydrogen.
 There is also a overlap of the sp2 hybridized orbital between the two carbon (yes, the C-C double bond has one sigma bond). This sigma bond here is shorter than the sigma bond fond in ethane because it has more s character (sp2 hybridized) than the sp3 hybridized.
There is also a overlap of the sp2 hybridized orbital between the two carbon (yes, the C-C double bond has one sigma bond). This sigma bond here is shorter than the sigma bond fond in ethane because it has more s character (sp2 hybridized) than the sp3 hybridized.
Pi Bond: There is an unhybridized p orbital in each carbon atom and they overlap to form a pi bond. The p orbitals have to be parallel to each other to overlap. This orientates the the C-H sigma bond in a plane. Also, a pi bond cannot rotate like a sigma bond does.
Orbitals
A double consists of one sigma bond and one pi bond. There are 4 electrons in a double bond.
A double consists of one sigma bond and one pi bond. There are 4 electrons in a double bond.
 Sigma Bond: There are 6 electrons in a carbon atom: 2 in the s orbitals and 4 in the p orbitals. Take a look of ethene, one carbon is bonded to a carbon and to two hydrogen atoms and there is no lone pair of electrons at the carbon. This implies a sp2 hybridization (120º bond angle). Each C-H sigma bond is the overlap of a sp2 hybridized orbital on carbon with the 1s orbital on hydrogen.
Sigma Bond: There are 6 electrons in a carbon atom: 2 in the s orbitals and 4 in the p orbitals. Take a look of ethene, one carbon is bonded to a carbon and to two hydrogen atoms and there is no lone pair of electrons at the carbon. This implies a sp2 hybridization (120º bond angle). Each C-H sigma bond is the overlap of a sp2 hybridized orbital on carbon with the 1s orbital on hydrogen. There is also a overlap of the sp2 hybridized orbital between the two carbon (yes, the C-C double bond has one sigma bond). This sigma bond here is shorter than the sigma bond fond in ethane because it has more s character (sp2 hybridized) than the sp3 hybridized.
There is also a overlap of the sp2 hybridized orbital between the two carbon (yes, the C-C double bond has one sigma bond). This sigma bond here is shorter than the sigma bond fond in ethane because it has more s character (sp2 hybridized) than the sp3 hybridized.Pi Bond: There is an unhybridized p orbital in each carbon atom and they overlap to form a pi bond. The p orbitals have to be parallel to each other to overlap. This orientates the the C-H sigma bond in a plane. Also, a pi bond cannot rotate like a sigma bond does.


Comments
Post a Comment